In this page you will find several techniques that will help you make your web content accessible.
Use alternative text with photos and images
- After you upload an image, with the image selected click on (more)
- Click on the “Add alt text” button
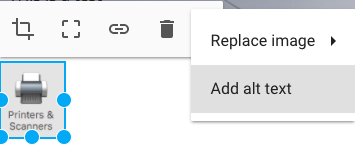
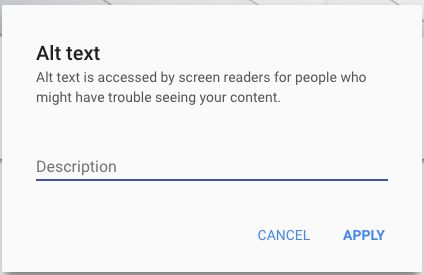
- Fill in the description field and click “apply”
Do not use animated Gifs or flashing elements
Animated GIFs or flashing elements can trigger seizures for some users of the website.
Do not solely use color to convey information
A good method to convey information without solely using color is to use text. Below is an example of the wrong way and the right way.
-
- Wrong way: Scheduled Test Date
- Right way: Important – Scheduled Test Date
Use Properly Labeled Links
Use links that make sense out of context. Publishers should avoid vague link phrases such as:
- Wrong way: click here
- Right way: Click here to visit the East Penn School District Website
iframes must be titled when embedding them to a website
Below is an example of embedding a google map without and with a title:
Without:
<iframe src=”https://calendar.google.com/calendar/embed?src=America/New_York” style=”border: 0″ width=”800″ height=”600″ frameborder=”0″ scrolling=”no”></iframe>
With:
<iframe title=”My Assignment Calendar” src=”https://calendar.google.com/calendar/embed?src=America/New_York” style=”border: 0″ width=”800″ height=”600″ frameborder=”0″ scrolling=”no”></iframe>
Website content that requires a special plugin or software must provide a source link
If your website contains a specific type of file, for example PowerPoint or PDF files, you must provide a link to the plugin or software.
Get Adobe Reader (note: This link can be placed in any accessible area of your website)
Time based content must provide a start, stop, pause or extend function
Below is an example of a slideshow with a pause button.

